In this series, I will study T-branes as they relate to F-theory in the context of GUT-model-construction. Aside: the book on the cover is a great read. Note that D-branes are crucial since they allow us to build various 4-D string theory vacua and dictate the phenomenology of compactifications as well. T-branes are non-Abelian deformation of intersecting D-brane systems in the corresponding compactification manifold. Without loss of generality, I will work in type IIB string theory compactified on a Calabi-Yau threefold ![]() quotiented by an orientifold action stacks of D3-branes and D7-branes. The BPS conditions are functionals:
quotiented by an orientifold action stacks of D3-branes and D7-branes. The BPS conditions are functionals:
![]()
![]()
and in 4-D are interpreted as a superpotential and D-term for each D7-brane.
and generally, the second quantized integral of the D-brane partition function for closed strings is given by:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[P_{{\rm{int}}}^{Dp} \equiv \not Z = \sum\limits_{\gamma = 0}^\infty {\underbrace {\int {{D^K}\gamma {{D'}^K}X{e^{S_{cld}^s}}} }_{{\rm{Topologies}}}} \]](https://www.georgeshiber.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f3e2dd4bb20cc6f54423fe585ae2392b_l3.png)
with a non-Abelian D-term:
![]()
and
![]()
is the first Pontryagin class-term, and ![]() is the flat space Kähler form:
is the flat space Kähler form:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[J = \underbrace {\frac{i}{2}{\rm{dx}} \wedge {\rm{d\bar x + }}\frac{i}{2}{\rm{dy}} \wedge {\rm{d\bar y}}}_{ = :\omega } + 2i{\rm{dz}} \wedge {\rm{d\bar z}}\]](https://www.georgeshiber.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-417733ad7b8551d8b3173be9dd53eec2_l3.png)
where ![]() in:
in:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[P_{{\rm{int}}}^{Dp} \equiv \not Z = \sum\limits_{\gamma = 0}^\infty {\underbrace {\int {{D^K}\gamma {{D'}^K}X{e^{S_{cld}^s}}} }_{{\rm{Topologies}}}} \]](https://www.georgeshiber.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f3e2dd4bb20cc6f54423fe585ae2392b_l3.png)
is given by:
![]()
In this, part one, I will show that the 7-brane superpotential for F-theory and the corresponding F-term conditions are purely topological and in no need for ![]() -corrections.
-corrections.
Recalling that a central class of T-brane configurations feature a Higgs field ![]() and a set of non-commuting generators
and a set of non-commuting generators ![]() as well as a non-primitive worldvolume flux of the form:
as well as a non-primitive worldvolume flux of the form:
![]()
which is a solution to the D-brane equation, and ![]() is the Cartan generator of the gauge group
is the Cartan generator of the gauge group ![]() and
and ![]() is a function of the 7-brane coordinates that solves the D-brane equation. The central problem of this series of posts is that this Abelian profile for
is a function of the 7-brane coordinates that solves the D-brane equation. The central problem of this series of posts is that this Abelian profile for ![]() needs the
needs the ![]() -correction for 4-D compactificational Calabi-Yau consistency conditions.
-correction for 4-D compactificational Calabi-Yau consistency conditions.
First, note that the Kähler form ![]() and:
and:
![]()
a holomorphic (3,0)-form in ![]() , satisfy:
, satisfy:
![]()
with ![]() the worldvolume flux and
the worldvolume flux and ![]() . Hence,
. Hence,
the pull-back on the D7-brane worldvolume is
![]()
where ![]() is a coordinate on
is a coordinate on ![]() .
.
The non-Abelian profiles for ![]() and
and ![]() must satisfy the 7-brane functional equations of motion. Non-Abelian generalisation of:
must satisfy the 7-brane functional equations of motion. Non-Abelian generalisation of:
![]()
![]()
are built up as follows. Write locally:
![]()
and localize the integral in:
![]()
as:
![]()
thus,
the non-Abelian generalisation of 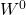 and
and 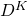 have both the form of the D7-brane Chern-Simons action and hence satisfy the T-brane equation of motion
have both the form of the D7-brane Chern-Simons action and hence satisfy the T-brane equation of motion
So effectively, we have a Kähler-equivalence of the derivatives in the pull-back with gauge-covariant ones, yielding:
![]()
![]()
with ![]() the inclusion of the complex Higgs field
the inclusion of the complex Higgs field ![]() , and
, and ![]() represents the symmetrization over gauge indices.
represents the symmetrization over gauge indices.
In this local description, the Higgs field is given by:
![]()
where ![]() is a matrix in the complexified adjoint representation of
is a matrix in the complexified adjoint representation of ![]() and
and ![]() its Hermitian conjugate. Thus, locally, we have:
its Hermitian conjugate. Thus, locally, we have:
![]()
with:
![]()
a Kähler coordiante expansion of ![]() and gives us, after inserting it in:
and gives us, after inserting it in:
![]()
the following:
![]()




2 Responses
T-Branes and F-Theory: α’- Corrections and the D-Term-Equations
Sunday, September 18, 2016[…] I last introduced T-branes, which are non-Abelian deformation of intersecting D-brane systems in the corresponding compactification manifold. Then I showed that we have a Kähler-equivalence of the derivatives in the pull-back with the gauge-covariant ones, which gave us: […]
Deriving 4D De Sitter Space from T-Branes via D7-Brane Action
Friday, December 16, 2016[…] Building on my earlier work on T-branes and F-theory, here I will show how De Sitter space emerges from an expansion of the D7-brane action around a T-brane background in the presence of 3-form supersymmetry breaking fluxes: this is crucial since de Sitter space is unstable in quantum gravity, while a D7-brane action resolves the instability. "T-branes are a non-abelian generalization of intersecting branes in which the matrix of normal deformations is nilpotent along some subspace", and it is truly remarkable that "the simplest heterotic string compactifications are dual to T-branes in F-theory." Recalling that the pull-back on the D7-brane worldvolume is given by: […]